Metal Forging Process
When buyers must select a process and supplier for the production of a critical metal component, they face an enormous array of possible alternatives. Many metalworking processes are now available, each offering a unique set of capabilities, costs and advantages. The forging process is ideally suited to many part applications; however, some buyers may be unaware of the exclusive benefits available only from this form of metal forming. In fact, forging is often the optimum process, in terms of both part quality and cost, especially for applications that require maximum part strength, custom sizes or critical performance specifications.
There are several forging processes available, including impression or closed die, cold forging, and extrusion. However, here we will discuss in detail the methods, application and comparative benefits of the open die and seamless rolled ring forging processes. We invite you to consider this information when selecting the optimum process for the production of your metal parts.
A historical perspective on metal forging
To meet the changing needs of industry, forging has evolved to incorporate the tremendous advances in equipment, robotics, computers and electronic controls that have occurred in recent years. These sophisticated tools complement the creative human skills which, even today, are essential to the success of every metal forging made. Modern forging plants are capable of producing superior-quality metal parts in a virtually limitless array of sizes, shapes, materials and finishes.
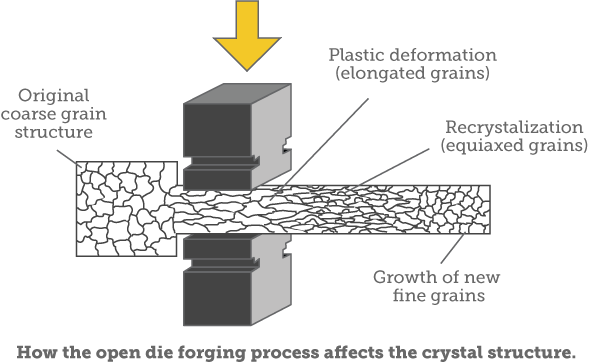
During this hot forging process, the cast, coarse grain structure is broken up and replaced by finer grains. Shrinkage and gas porosity inherent in the cast metal are consolidated through the reduction of the ingot, achieving sound centers and structural integrity. Mechanical properties are therefore improved through reduction of cast structure, voids and segregation. Forging also provides means for aligning the grain flow to best obtain desired directional strengths. Secondary processing, such as heat treating, can also be used to further refine the part.
Forging can create a myriad of sizes and shapes with enhanced properties when compared to castings or assemblies.
Go to next section: The open die forging process